Understanding Diabetes: A Complete Guide to Management
Understanding Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces, resulting in high blood sugar levels. While diabetes can be managed, it requires ongoing effort to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
This guide will provide a thorough understanding of diabetes, its different types, and the most effective strategies for managing the condition. From diet and exercise to medication and lifestyle changes, we’ll explore practical tips that can help individuals living with diabetes lead a healthy and fulfilling life.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that involves problems with insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar. There are two main types of diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This type is usually diagnosed in children and young adults. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage their blood sugar levels.
2. Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes and occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin. It is often linked to lifestyle factors, such as being overweight, lack of physical activity, and poor diet. Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be managed with diet and lifestyle changes, but many people also need medication or insulin to control their blood sugar levels.
3. Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth. However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
4. Prediabetes:
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. With early intervention, such as changes in diet and exercise, it is possible to prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes.
Key Strategies for Managing Diabetes
Effective diabetes management involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring. Let’s dive into the key components of a comprehensive diabetes management plan.
1. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
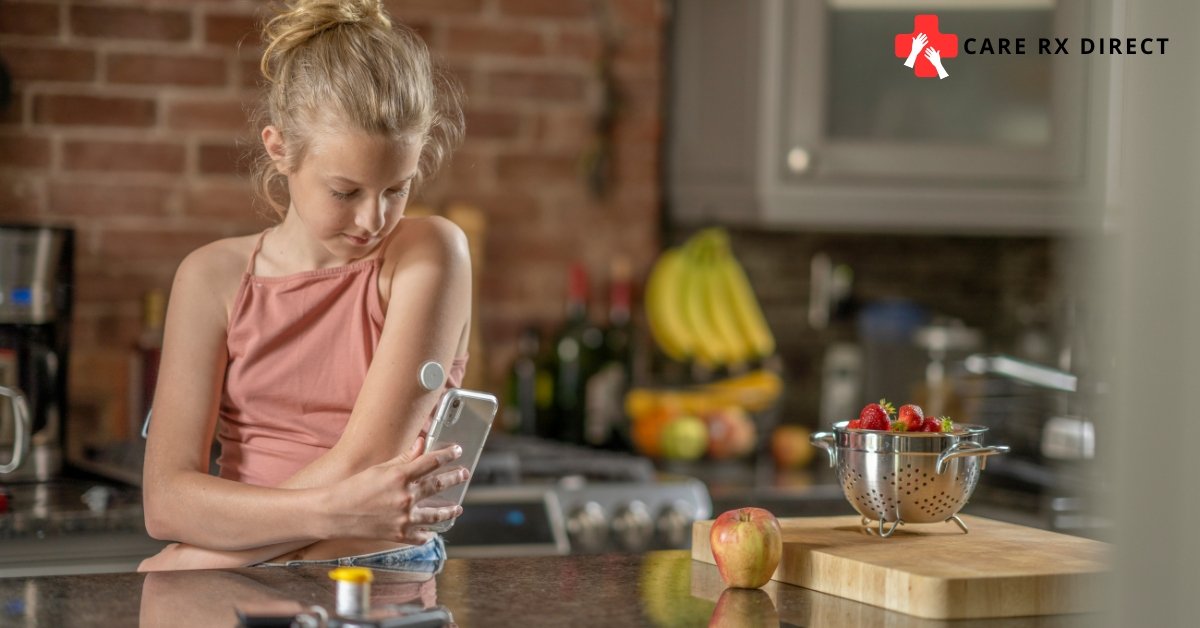
One of the most important aspects of diabetes management is regularly monitoring blood sugar levels. Keeping track of blood sugar helps individuals understand how their body responds to food, exercise, medication, and other factors. By maintaining blood sugar within a target range, people with diabetes can reduce the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
How to monitor blood sugar:
- Self-monitoring: Individuals can use a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) to check their blood sugar levels regularly.
- Frequency: The frequency of blood sugar checks depends on the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and physician recommendations. For some, daily checks are necessary, while others may only need to check once or twice a week.
2. Healthy Eating for Blood Sugar Control
Diet plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. Eating a balanced diet that focuses on whole foods, fiber, and low-glycemic index (GI) foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels. It is important to avoid excessive amounts of sugar and refined carbohydrates, as these can cause spikes in blood sugar.
Key dietary tips include:
- Focus on fiber-rich foods: Whole grains, vegetables, and legumes help regulate blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Eat smaller, balanced meals: Rather than consuming large meals, smaller, well-balanced meals throughout the day can help maintain consistent blood sugar levels.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks: Avoid processed sugars, sodas, and snacks that can quickly raise blood sugar levels.
- Healthy fats: Incorporating sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can help improve heart health and blood sugar control.
Example of a diabetes-friendly meal plan:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with chia seeds, berries, and a handful of almonds.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, olive oil, and a side of quinoa.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with steamed broccoli and a small portion of brown rice.
3. Physical Activity and Exercise
Regular physical activity is essential for people with diabetes, as it helps improve insulin sensitivity, manage blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of complications. Exercise helps muscles use glucose more effectively, which lowers blood sugar levels.
Exercise guidelines for diabetes management:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Strength training: Incorporating strength training exercises twice a week can improve muscle mass and enhance insulin sensitivity.
- Flexibility and balance: Activities like yoga or Pilates can improve flexibility and balance, reducing the risk of falls and improving overall mobility.
4. Medication and Insulin Therapy
While many people with type 2 diabetes can manage their condition with lifestyle changes alone, others may require medication to help control their blood sugar. In type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is always necessary.
Common medications include:
- Metformin: A first-line medication for type 2 diabetes, which helps reduce glucose production in the liver and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: These drugs help the pancreas produce more insulin.
- GLP-1 agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors: Newer medications that help control blood sugar by improving insulin production and preventing sugar from being reabsorbed by the kidneys.
- Insulin therapy: For people with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2 diabetes, insulin injections or an insulin pump may be necessary to regulate blood sugar levels.
Insulin management tips:
- Work with a healthcare provider to find the right type and dosage of insulin.
- Use an insulin pump or multiple daily injections based on personal needs and lifestyle.
- Consider options like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) to track blood sugar levels in real-time and adjust insulin doses accordingly.
5. Stress Management and Sleep
Chronic stress and poor sleep can negatively impact blood sugar control. Managing stress is essential to diabetes management, as stress hormones like cortisol can increase blood sugar levels.
Stress management tips include:
- Mindfulness and meditation: Practicing mindfulness, deep breathing, or yoga can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Adequate sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night, as sleep deprivation can interfere with blood sugar regulation.
6. Regular Checkups and Monitoring Complications
People with diabetes need regular checkups to monitor their health and address any potential complications. Common complications associated with diabetes include cardiovascular disease, nerve damage (neuropathy), kidney disease (nephropathy), and eye problems (retinopathy).
Important checkups include:
- A1C test: This test measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months and helps determine long-term control.
- Blood pressure and cholesterol: Regular checks to assess cardiovascular health.
- Foot exams: To prevent complications related to nerve damage and poor circulation.
- Eye exams: To monitor for diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can lead to vision loss.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes is a lifelong commitment, but with the right strategies, it’s possible to live a healthy, active life. By focusing on blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, regular exercise, medication, stress management, and regular checkups, individuals with diabetes can maintain good control over their condition and reduce the risk of complications.
If you have diabetes or are at risk, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to create a personalized management plan that meets your unique needs.

54 Replies to “Understanding Diabetes: A Complete Guide to Management”
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/vi/register?ref=WTOZ531Y
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/join?ref=P9L9FQKY
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.com/vi/register-person?ref=WTOZ531Y
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.info/register?ref=P9L9FQKY
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.com/ur/register?ref=WTOZ531Y
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.